Parasitic worm infections, also known as helminth infections, are caused by various species of worms that live in the human body. These infections are prevalent worldwide, particularly in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene. Common types of parasitic worms include roundworms, tapeworms, flukes, and hookworms. The diagnosis of parasitic worm infections is essential for determining appropriate treatment and preventing complications. In this article, we will explore the methods used to diagnose these infections and discuss the role of medications such as Nizonide 500 mg in treatment.
Overview of Parasitic Worm Infections
Parasitic worm infections affect millions of people globally. These infections are typically contracted through the ingestion of contaminated food or water, contact with infected soil, or poor hygiene practices. The symptoms of worm infections vary depending on the type of parasite, the location of the infection, and the severity. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Malnutrition
Itching around the anus (especially in cases of pinworm infection)
Due to the non-specific nature of these symptoms, diagnosing parasitic worm infections often requires laboratory testing and clinical evaluation.
Diagnostic Methods for Parasitic Worm Infections
1. Stool Examination
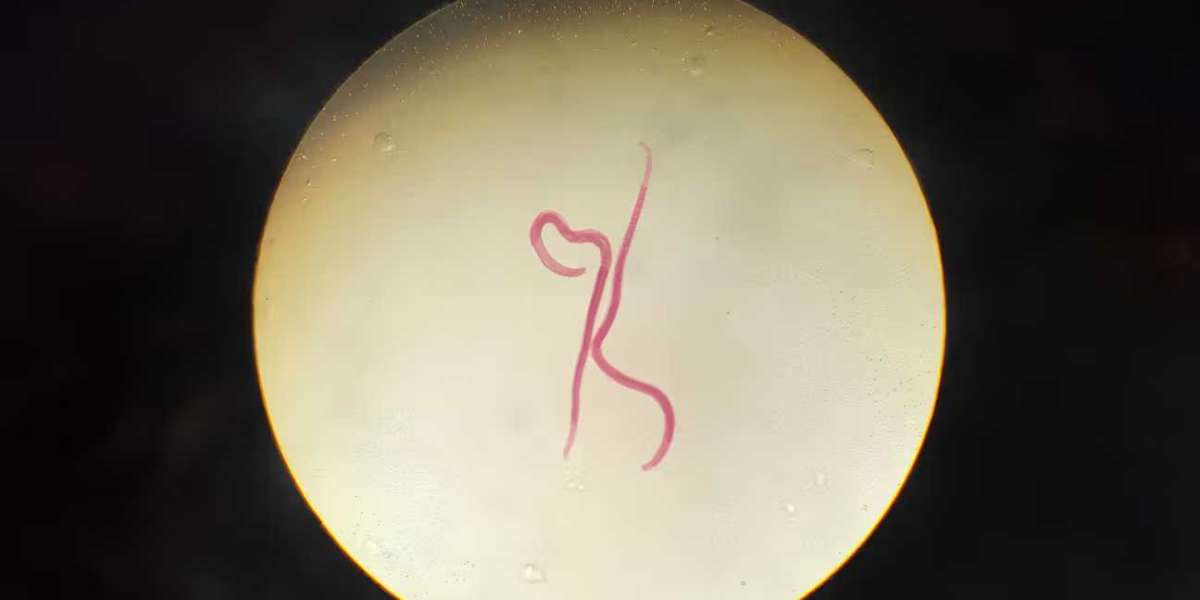
One of the most common and straightforward methods for diagnosing parasitic worm infections is stool examination. Since many worms lay eggs or shed segments into the intestines, these can often be detected in a patient's stool sample. A fecal sample is examined under a microscope to identify the presence of worm eggs, larvae, or adult worms.
Ova and Parasite (OP) Test
This test involves examining the stool sample for the eggs (ova) of parasites and the parasites themselves. Several samples might be needed over a period to increase the likelihood of detecting the parasites, as they may not be present in every sample.
Concentration Methods
In some cases, stool samples are treated with chemicals to concentrate the eggs or larvae, making them easier to detect under the microscope.
Stool Antigen Test
This test looks for specific antigens produced by the parasites in the stool, offering a more sensitive and specific method of detecting certain parasitic infections, such as giardiasis.
2. Blood Tests
Blood tests can also be used to diagnose parasitic worm infections, particularly in cases where the parasites migrate through the bloodstream or affect organs outside of the intestines. The following are common blood tests used for diagnosis:
Eosinophil Count
Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell that often increases in response to parasitic infections. An elevated eosinophil count can suggest the presence of a parasitic infection, though it is not specific to worms.
Serological Tests
These tests detect antibodies or antigens in the blood that indicate the presence of a parasitic infection. For example, serological tests can be used to diagnose infections caused by liver flukes, schistosomes, and trichinella worms.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Testing
PCR testing can detect the genetic material of parasites in the blood or stool, offering a highly sensitive and specific method of diagnosis. It is particularly useful for detecting infections caused by parasites that are difficult to identify through microscopy.
3. Imaging Techniques
In some cases, parasitic worms can cause damage to organs, and imaging techniques may be used to detect the presence of parasites or the effects of the infection. These techniques are usually employed when the infection involves tissues or organs outside the intestines.
Ultrasound
This imaging technique can be used to detect parasitic cysts in organs such as the liver, lungs, or brain. For example, cystic echinococcosis, caused by the tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus, can lead to the formation of cysts that can be seen on ultrasound.
CT Scan or MRI
Computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help identify damage to tissues and organs caused by parasitic infections, such as in cases of neurocysticercosis (a brain infection caused by the pork tapeworm).
4. Endoscopy or Colonoscopy
For infections affecting the intestines or other parts of the digestive tract, doctors may use endoscopy or colonoscopy to directly visualize the parasites. In these procedures, a thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth or rectum to examine the digestive tract and collect tissue samples for further analysis. This method is particularly useful for diagnosing infections caused by large worms like hookworms or tapeworms.
5. Biopsy
In some cases, tissue samples may be required for a definitive diagnosis of a parasitic worm infection. A small piece of tissue is removed and examined under a microscope to detect the presence of parasites. This method is often used for diagnosing infections that affect organs or tissues outside the intestines, such as trichinosis, where the worms encyst in muscle tissue.
Treatment of Parasitic Worm Infections
Once diagnosed, parasitic worm infections can be treated with antiparasitic medications. The choice of medication depends on the type of parasite and the severity of the infection. Nizonide 500 mg is one such medication commonly used in the treatment of parasitic infections, particularly those caused by protozoan parasites like Giardia lamblia and Entamoeba histolytica. However, it may also be effective against certain helminth infections.
Nizonide 500 mg
This medication contains nitazoxanide 500mg, an antiparasitic agent that works by interfering with the energy production of parasites, ultimately leading to their death. It is commonly prescribed for the treatment of giardiasis, cryptosporidiosis, and amoebiasis. While its primary use is for protozoan infections, it may also have activity against certain worm infections. However, for specific helminth infections, other medications like albendazole, mebendazole, or ivermectin may be more appropriate.
Albendazole and Mebendazole
These medications are commonly used to treat a wide range of helminth infections, including roundworms, hookworms, and tapeworms. They work by inhibiting the ability of worms to absorb sugar, leading to their eventual death.
Ivermectin
This medication is effective against a variety of parasitic worms, including strongyloides and onchocerciasis (river blindness). It works by paralyzing the worms, making them easier for the body to expel.
Praziquantel
This medication is used to treat infections caused by tapeworms and schistosomes. It works by damaging the worm’s skin, causing paralysis and death.
Prevention and Control of Parasitic Worm Infections
Preventing parasitic worm infections requires a combination of personal hygiene, sanitation, and public health measures. Some key preventive strategies include:
- Washing hands regularly with soap and water
- Properly cooking food and drinking clean water
- Avoiding contact with contaminated soil or water
- Wearing shoes in areas where hookworm infection is common
- Practicing good personal hygiene, especially in households with children
Public health programs that promote deworming in endemic areas can significantly reduce the burden of parasitic worm infections, particularly in children.
Conclusion
Diagnosing parasitic worm infections involves a variety of methods, including stool examination, blood tests, imaging, and endoscopy. These diagnostic tools help healthcare professionals identify the specific parasite causing the infection and determine the appropriate treatment. Nizonide 500 mg is one of the medications used to treat parasitic infections, particularly protozoan infections, but other medications may be necessary for treating helminth infections. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and improve patient outcomes.